How to set up a AWS EC2 Instance in VSCode
I will explain how to connect to a remote machine to VSCode. The remote machine will be a ubuntu server in a AWS instance that, in my case, will be used to run lightweight ml models.
1. Create an AWS instance
First, just google AWS, create an account, and you will see the option to create an instance in the main page.
Free accounts have a free tier. Selecting everything with the "Free tier eligible" should be free, but please take care what you launch anyway and do not select a 98 Ram machine with a Tesla V100 GPU and whatnot unless you know what you doing.
Here I will set up a cheap machine (like $0.1/hour):
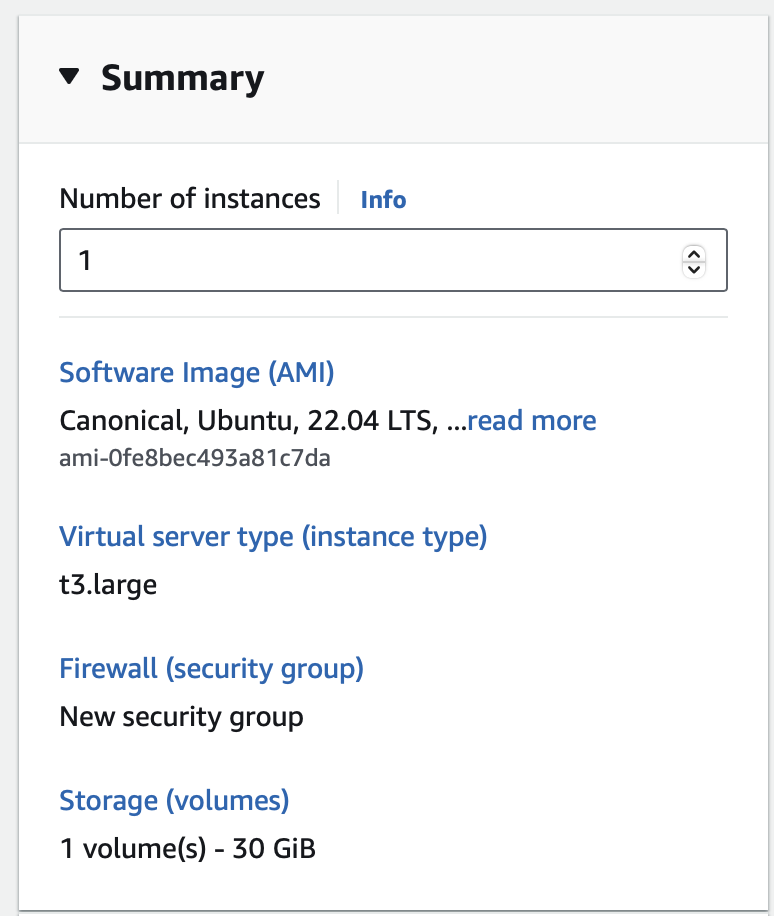
OS: Ubuntu Server 22.4 64-bit (x86)
Image: t3.large or t3.xlarge (8/16 Gb of RAM)
Key pair: New key -> place the pem file in the directory under your ~/.ssh/ folder (I called mine mlops_key):
Network settings: Allow SSH traffic from “Anywhere”. As long as you configure the key pair you should be okay.
Storage: 30 Gb
If the SSH key file was placed correctly, you can access the machine via ssh using the Public PIv4 address you can find in your instance summary website:
ssh -i ~/.ssh/mlops_key.pem ubuntu@{Instance public IPv4 address}
P.S. I did have a problem the first time I tried to connect with "permissions being too open":
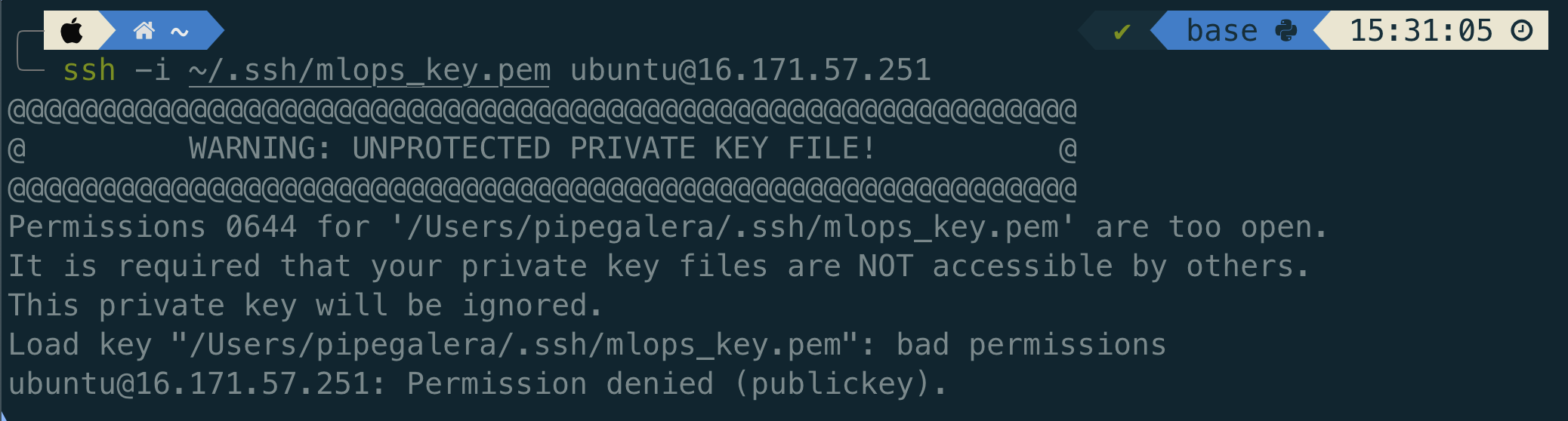
That can be solved by running chmod 600 ~/.ssh/mlops_key.pem (Source)
We would like to avoid typing the IP of the virtual OS every time we connect to the instance and simply connect typing "ssh mlops", for example.
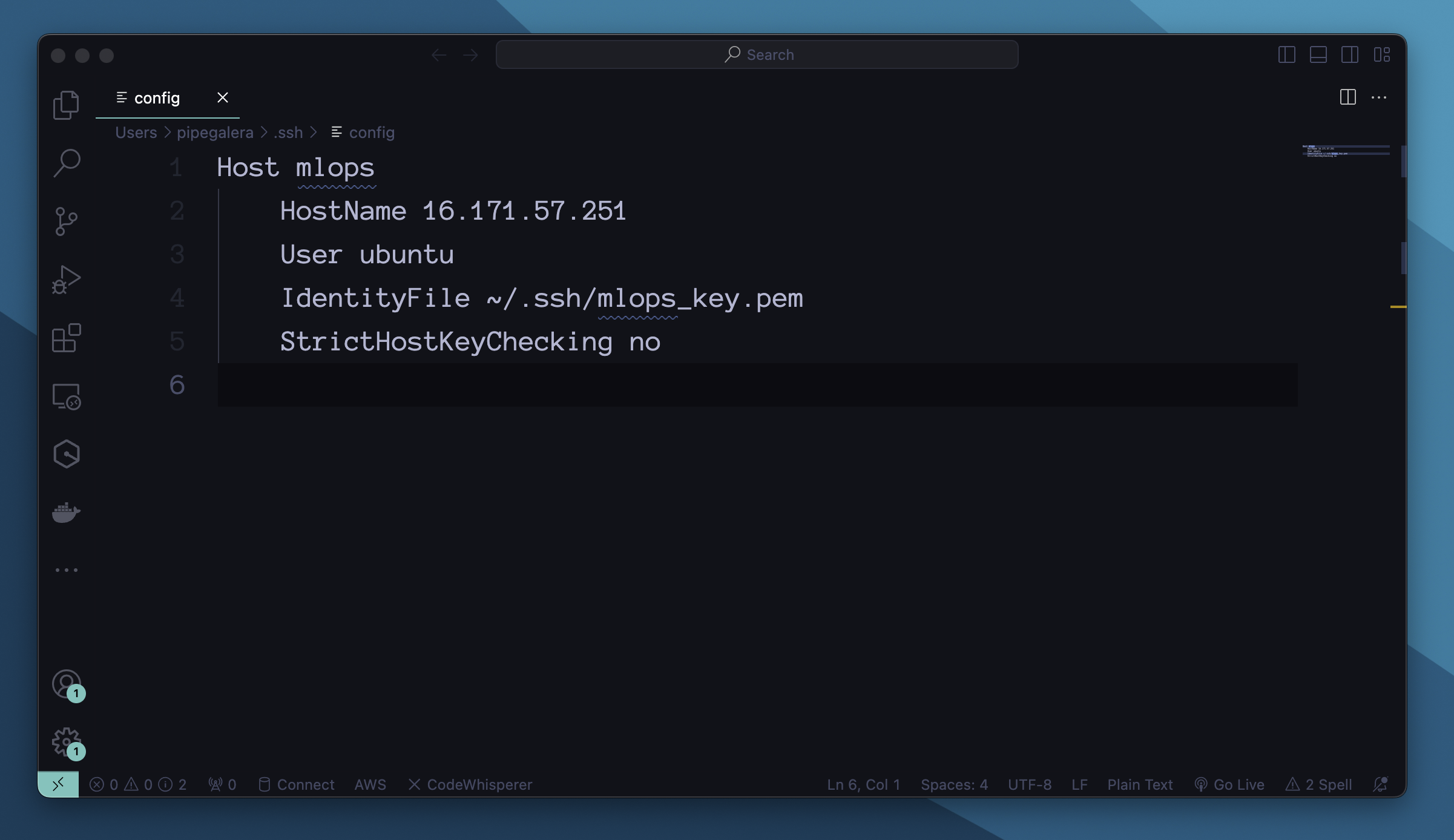
To create this shortcut, modify the config file under ssh or your local machine:
Host mlops
HostName {Instance public IPv4 address}
User ubuntu
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/mlops_key.pem
StrictHostKeyChecking no
E.g.:
2. Install stuff in the ubuntu OS
- Docker
# Update apt
sudo apt update
# Install docker and docker-compose
sudo apt install docker.io docker-compose
# To us docker without using sudo continuously
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
- Miniconda
# Download miniconda
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
# Run the installer
bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -b
# Add Anaconda to the system path
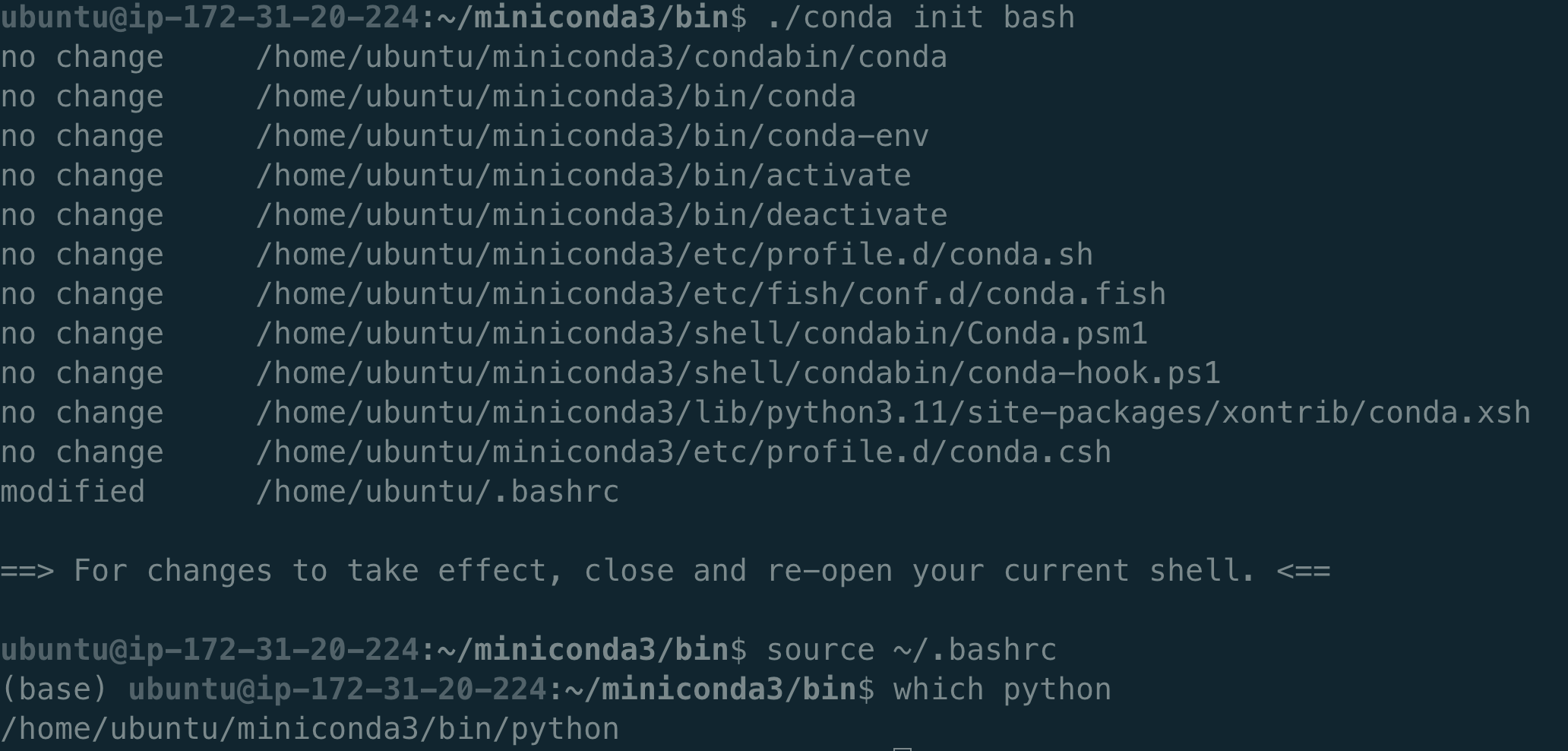
cd miniconda3/bin
./conda init bash
After this, “which python” should point out to the anaconda version:
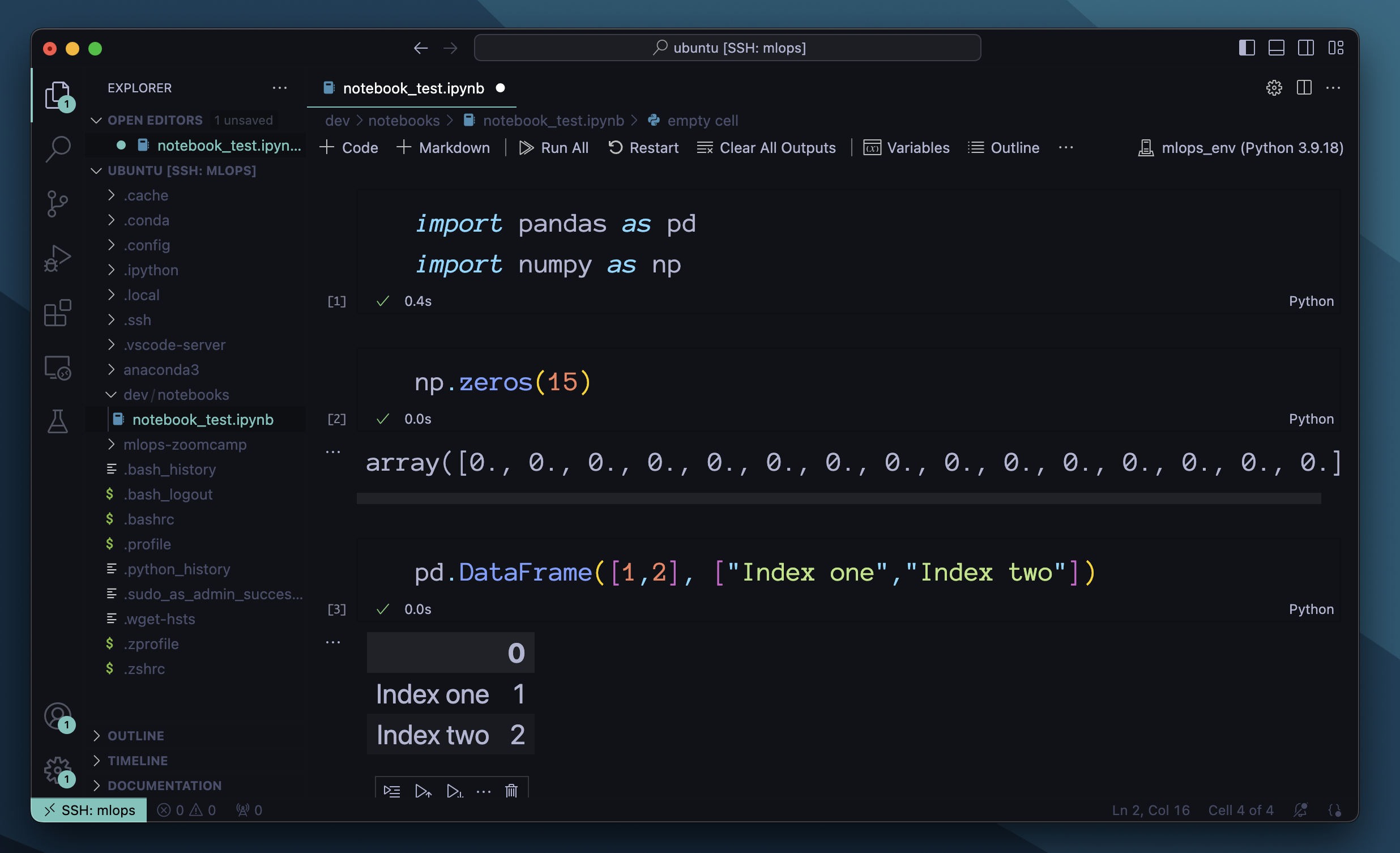
3. Configure VSCode
Open VSCode locally and install the following:
Install Remote-SSH: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/ssh-tutorial
Install Jupyter: https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-toolsai.jupyter
Open Command Palette(Cmd+Shift+P) and search "Connect host" and it will pop up:
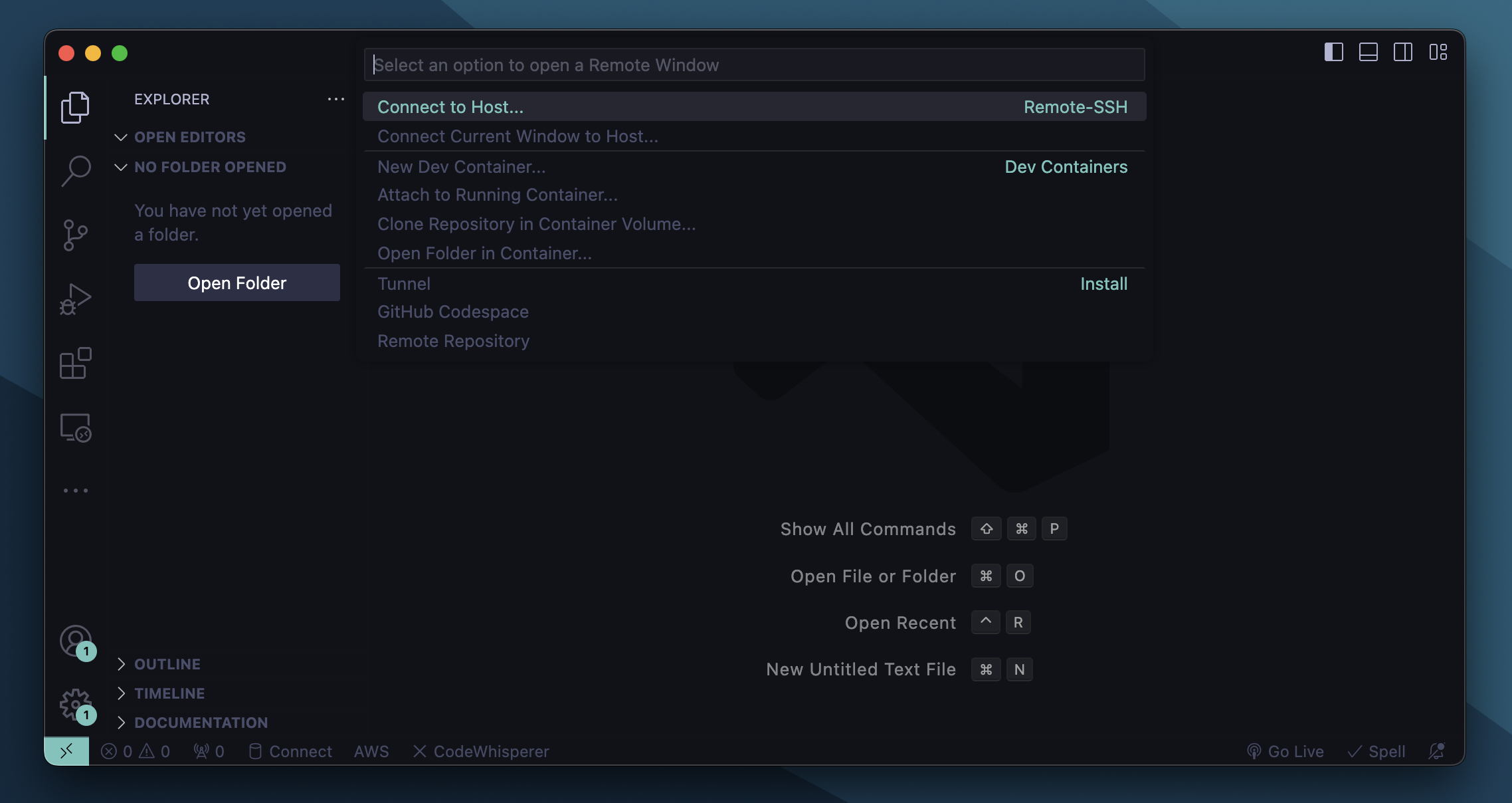
It will automatically read the Host from the .ssh/config file:

And that's it, you have VSCode connected to remote ubuntu machine.
Clicking open folder will load a tree view. From there you can easily organize files, drag&drop files from your local computer to the folders in the remote machine, or create new files. Like you would locally.

Please remember to stop the instance in AWS to avoid getting charged while not using it.